Rechenoperationen
Grundrechenarten durchführen
Im letzten Abschnitt hast du die Datentypen Int und Float zur Zahldarstellung in Elm kennengelernt.
Mit den Daten dieser beiden Datentypen kann man die gängigen Rechenoperationen durchführen.
Beispieldialog 1:
> 5+2
7 : number
> 5-2
3 : number
> 5*2
10 : number
> 5/2
2.5 : Float
> 5//2
2 : Int
Beispieldialog 2:
> 6.2 + 2
8.2 : Float
> 6.2 - 2
4.2 : Float
> 6.2 * 2
12.4 : Float
> 6.2 / 2
3.1 : Float
> 6.2 // 2
-- TYPE MISMATCH ---------------------------------------------------------- REPL
The (//) operator is specifically for integer division:
3| 6.2 // 2
^^^
The left side of (//) must be an Int, but I am seeing a Float. I recommend doing
the conversion explicitly with one of these functions:
round 3.5 == 4
floor 3.5 == 3
ceiling 3.5 == 4
truncate 3.5 == 3
Note: Read <https://elm-lang.org/0.19.1/implicit-casts> to learn why Elm does
not implicitly convert Ints to Floats.
Beispieldialog 3:
> 6.0 + 3.0
9 : Float
> 6.0 - 3.0
3 : Float
> 6.0 * 3.0
18 : Float
> 6.0 / 3.0
2 : Float
> 6.0 // 3.0
-- TYPE MISMATCH ---------------------------------------------------------- REPL
The (//) operator is specifically for integer division:
3| 6.0 // 3.0
^^^
The right side of (//) must be an Int, but I am seeing a Float. I recommend
doing the conversion explicitly with one of these functions:
round 3.5 == 4
floor 3.5 == 3
ceiling 3.5 == 4
truncate 3.5 == 3
Note: Read <https://elm-lang.org/0.19.1/implicit-casts> to learn why Elm does
not implicitly convert Ints to Floats.
-- TYPE MISMATCH ---------------------------------------------------------- REPL
The (//) operator is specifically for integer division:
3| 6.0 // 3.0
^^^
The left side of (//) must be an Int, but I am seeing a Float. I recommend doing
the conversion explicitly with one of these functions:
round 3.5 == 4
floor 3.5 == 3
ceiling 3.5 == 4
truncate 3.5 == 3
Note: Read <https://elm-lang.org/0.19.1/implicit-casts> to learn why Elm does
not implicitly convert Ints to Floats.
Aufgabe 1
Probiere das selbst aus und deute die Ergebnisse.
Aufgabe 2
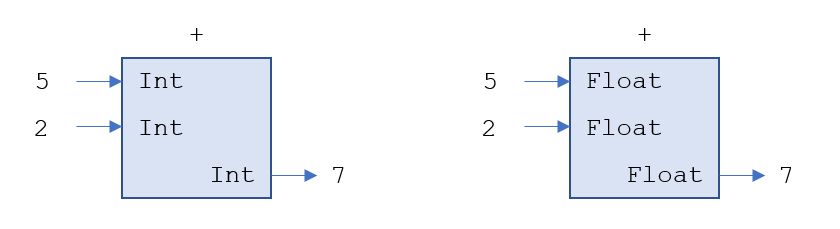
(a) Erkläre anhand der folgenden Diagramme, dass der Plusoperator + aus zwei Int-Zahlen immer eine Int-Zahl erzeugt und
analog aus zwei Float-Zahlen immer eine Float-Zahl erzeugt.
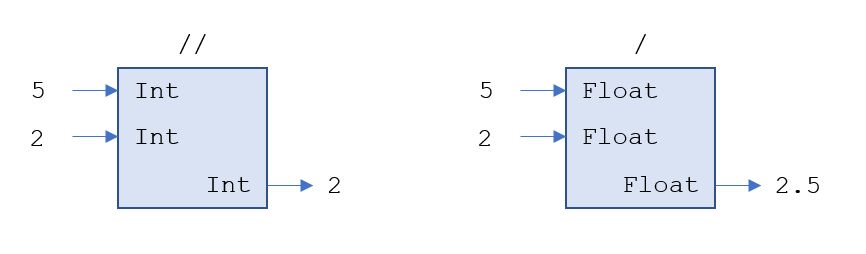
(b) Erkläre anhand der folgenden Diagramme, dass es für die Division unterschiedliche Operatoren für Int-Zahlen und Float-Zahlen gibt.
Quellen
- [1]: Plusoperator - Urheber: KB - Lizenz: inf-schule.de
- [2]: Divisionsoperatoren - Urheber: KB - Lizenz: inf-schule.de